& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
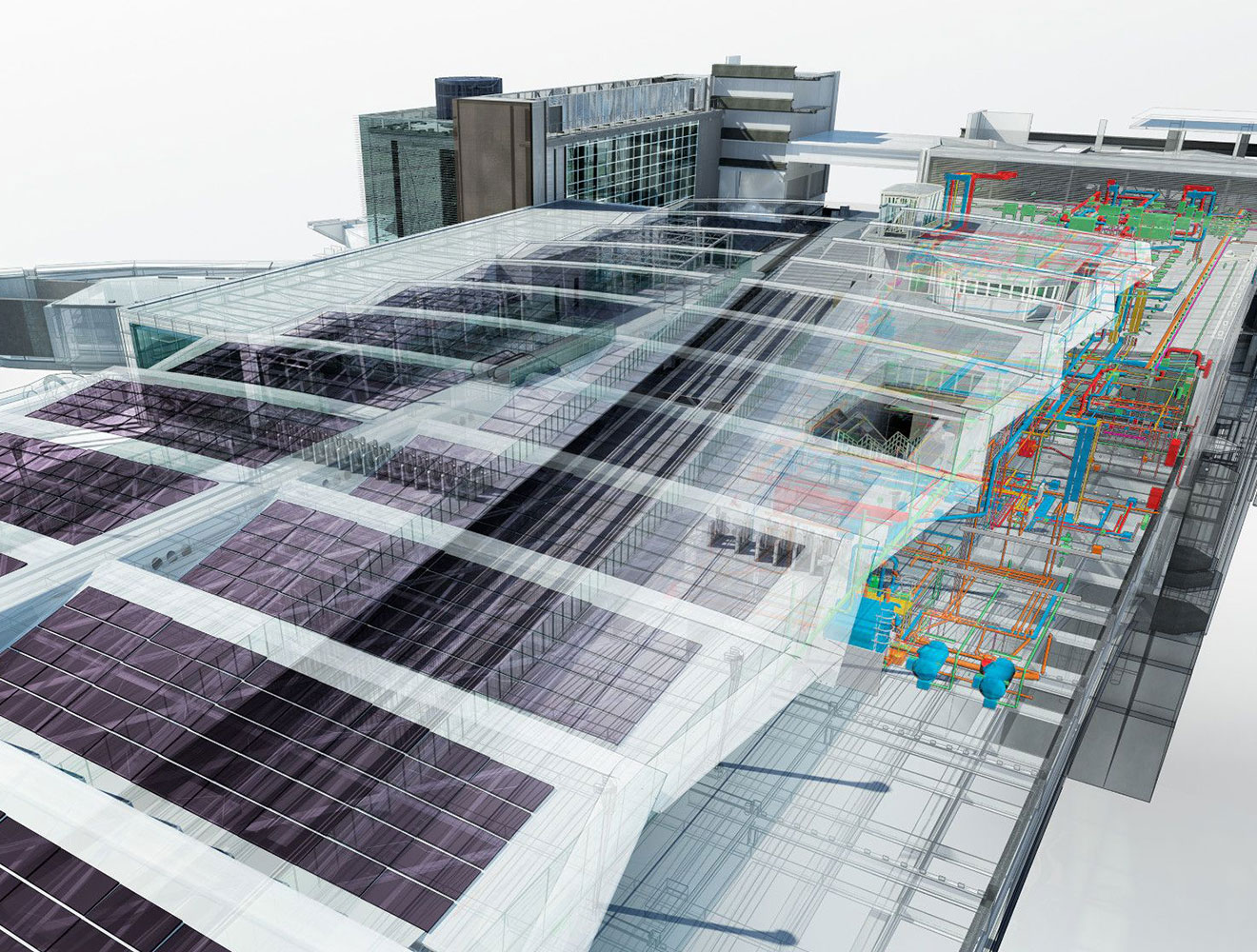
Building simulation software is a 3D, computer-based model that replicates real-world conditions to analyze how they would affect a building in a real scenario. Engineers, architects, and designers can use the simulation to optimize aspects of a building’s performance, including energy usage, thermal comfort, lighting, and environmental impact. Architects and engineers use building performance simulation tools to assess and refine designs before construction begins. This encourages informed decisions and more efficient and sustainable built environments.
You can use building simulation software to imitate various elements and understand how they interact with your proposed project, as well as pre-existing constraints.
Building energy simulation models energy consumption and performance to optimize building energy efficiency, assessing the impact of design choices, HVAC systems, and insulation of energy usage.
This type of building performance simulation evaluates the thermal performance of a building, analyzing factors such as heat flow, temperature distribution, and thermal comfort. Thermal simulation helps design spaces that maintain optimal temperatures with minimal heating or cooling.
A type of building simulation software that determines how to combine sunlight and shading to make occupants comfortable and reduce artificial lighting needs. Daylight simulation can also reduce the demand for energy used within buildings.
Here, the software models how air moves within the proposed structure so designers can create efficient ventilation and ensure high air quality indoors. Airflow simulation can also reduce costs and overall energy consumption.
A type of building performance simulation that examines the impact of solar radiation on a building’s performance. This method evaluates shading, solar heat gain, and the potential for integrating solar energy solutions.
Architects can use acoustic simulation to model and replicate the impact of ambient sound in a building. It allows for the optimization of soundscapes and is especially useful for those designing and building large spaces like concert halls.
An advanced building simulation technique that emulates how fire and smoke could spread within a space. Fire and smoke simulation aims to increase survivability and improve evacuation strategies.
Assessing structures like bridges and skyscrapers, structural load analysis focuses on the stresses of a structure to predict the structural integrity of a building for general aging and natural disasters.
Predicts heating, cooling, and airflow loads to optimize building mechanical, ventilation, and HVAC systems for efficiency and comfort.
Building simulation can only be as accurate as the inputted data. Everything from the data source, format, and validity must be input and output perfectly for effective results. If the quality of the data is poor, it can lead to errors in the simulation process, damaging the reliability of the results.
London Blackfriars station, courtesy of Network Rail and Jacobs(r)
It’s important that those using building simulation software have the skills and knowledge to use it well. This requires strong technical and analytical skills, as well as a strong understanding of the construction and architecture industries. To avoid mistakes in software usage, your team must be able to use the technology to its full potential.
Building simulation software encourages precise decisions for critical aspects of the preconstruction process. It gives engineers, architects, and designers a clear idea of how real-life scenarios will affect their structure so they can design with resilience in mind.
Simulation software provides a detailed and accurate platform for analyzing critical aspects of a building, including energy efficiency, thermal comfort, and lighting. This precision helps designers enhance the usability of the building in a wide range of scenarios.
Engineers, architects, and designers can identify and rectify potential problems by using building performance simulation to emulate specific design scenarios. This reduces potential challenges that could come up in the future, reducing costs for modifications after construction.
With building energy simulation, you can reduce a structure's environmental impact before it’s too late. Building simulation software encourages sustainable design by implementing eco-friendly features at the beginning of the planning stage.
Use building simulation software to predict the comfortability of a building at any point in the year. Building energy simulation enables designers and architects to create a productive and more comfortable environment for those who will use the building.
Building performance software facilitates the detection of potential performance issues before they occur. Identify inadequate ventilation or thermal discomfort to address the challenges before construction begins.
Building performance simulation enables designers to ensure projects comply with industry standards and local regulations, as well as energy efficiency requirements.
Cloud software that offers powerful, easy-to-use, AI-powered tools for pre-design and schematic design. Making the right decisions in the planning phase has never been easier.
Powerful BIM and CAD tools for designers, engineers, and contractors, including Revit, AutoCAD, Civil 3D, Forma Site Design, and more
Plan, design, construct, and manage buildings with powerful tools for Building Information Modeling.
Browse Autodesk’s range of resources on building performance simulation for construction projects of all sizes.
In this paper, Autodesk Research scientists propose an end-to-end pipeline that uses graph neural networks to automate the structural design process for buildings, minimizing the material mass and satisfying building codes.
Learn how Autodesk’s CFD (computational fluid dynamics) suite enables design and construction consultancy Sudlows to simulate airflow, thermal footprints, and energy efficiency for data centers before construction commences.
BIM/VDC veteran Manuel Frey shows learners how he uses model-based building-performance simulations as an integral part of the planning process chain, from data management and quality control to analysis and visualization.
Our new guidebook explains how architects can integrate carbon analysis in the design process, and thereby more easily measure and mitigate carbon.
Autodesk Forma empowers architects with comprehensive, easy-to-use environmental impact analyses for pre-design and schematic design. Explore concepts and optimize living quality and sustainability.
Building simulation software is a type of computer program designed to model and analyze building performance factors, including energy usage, thermal comfort, lighting, and overall environmental impact.
Depending on the type and scope of the project, building simulations can be used to model energy usage, thermal performance, natural lighting, airflow, acoustics, occupant behavior, and structural integrity.
Virtual simulations can help architects, engineers, and designers model environmental impact; optimize projects for energy efficiency, thermal comfort, and lighting; and detect issues at the pre-construction stage. However, building simulations offer limited accuracy and can delay project kickoff because of the iterative process required.
Building simulation software generates an image of the building being designed using a CAD model (a digital representation). Based on the desired outcome, software tools are then chosen.
The software can be used to demonstrate performance-based compliance with building codes and standards, using your designs as a visual representation of your efforts.