& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Industrial engineering has its roots in the First Industrial Revolution and the rise of mass production. A famous early example is Henry Ford’s assembly line, which cut automobile production time from 700 to just 1.5 hours in 1913.
The field has since evolved, with movements like “total quality management” (TQM) in the West and “kaizen” in Japan pushing continuous improvement across industries.
Today, industrial engineering blends engineering expertise with scientific methods to streamline complex business systems, particularly in manufacturing. It focuses on optimizing time, energy, materials, and finances to help companies work smarter, not harder.
Industrial engineers use data analysis and process evaluation to drive innovation, reduce costs, and promote sustainability across sectors.
With advanced industrial engineering software, companies can be more productive, address inefficiencies, and build a more efficient future.
Industrial engineering is best known for revolutionizing assembly lines, but its methods extend far beyond that. The same principles apply to logistics, operations, and many other industrial systems.
In manufacturing, industrial engineers rely on data from machines and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to identify and fix inefficiencies on the assembly line. By analyzing real-time data, they improve machine performance while also ensuring the safety and comfort of workers. This approach helps them achieve critical goals: boosting process efficiency, predicting maintenance needs, and increasing overall productivity—all while lowering lifecycle costs.
For logistics and supply chain management, industrial engineering streamlines inventory flow, balancing costs with demand forecasts. It also rethinks warehouse design to maximize space and reduce handling times.
With manufacturing execution system (MES) software like Autodesk Fusion Operations, industrial engineers ensure smooth, adaptive supply chains by gaining real-time control over their data, which helps prevent disruptions.
By applying principles from physics, math, and even social sciences, industrial systems engineering informs decision-making across every part of a business—whether it’s equipment, facilities, materials, energy, finances, or workforce.
With the support of algorithms and machine learning, industrial engineering software creates new opportunities for automation, not just in manufacturing but also in areas like scheduling and financial planning.
While industrial engineering was once linked to manufacturing, its principles now support a wide range of industries that each benefit from improved systems.
In banking, industrial engineers transform operations by streamlining processes and improving service delivery. They can use careful analysis to allocate resources to the most appropriate possible place and make sure customers are always getting the best experiences.
Industrial engineering teams within the healthcare sector are central to managing patient flow and reducing wait times. By refining healthcare delivery systems, they can ensure their expertise is used effectively, leading to better, more efficient patient outcomes.
Transportation industries often use industrial engineering to improve their routing and logistics management. In a complex network of operations, teams must ensure their goods are delivered on time and within budget - optimized systems help them achieve this.
In retail companies, industrial engineers might use software to analyze supply chain dynamics and inventory management to create smooth shopping experiences. Insights into store layouts and delivery schedules result in more sales and happier, loyal customers.
Discover what the future holds for industrial engineering with these growing trends.
The power of computer simulation is on the rise. With tools like Autodesk FlexSim, industrial engineers can create digital twins of products, facilities and systems. These technologies allow them to test how things work and predict outcomes without any risk. By running thousands of discrete event simulations for less than the cost of a few real-world tests, engineers can find the best factory designs and processes.
Automation is changing the game in manufacturing and beyond. It takes over repetitive tasks, enabling workers to focus on improving efficiency and production. However, while automation can boost productivity, it also brings challenges like installation and maintenance that engineers must tackle. According to the US Bureau of Labour Statistics, this growing need for expertise drives a predicted 12% job growth for industrial engineers from 2022 to 2032.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping how we think about manufacturing. Although AI accelerates automation, it’s still a tool that requires human oversight. Industrial engineers will work alongside AI to unlock new levels of productivity and make smarter decisions. AI and industrial engineers are driving the future of industrial machine design, combining technology and expertise to create smarter manufacturing systems.
With a growing emphasis on sustainability worldwide, industrial engineers are stepping up to create eco-friendly practices. They focus on reducing environmental impact by optimizing energy use and material choices. Industries can improve their energy efficiency and resource management, meaning they can thrive using fewer resources.
Industrial engineers amplify their effectiveness with the right software, leading to benefits at every level—from production performance to system operations.
With dedicated industrial engineering software, engineers can optimize products to meet higher quality standards. This not only raises customer satisfaction but also builds lasting loyalty.
Whether for supply chains, cost management, or facility oversight, industrial engineering software maximizes the efficiency of entire systems. Up-to-the-minute data insights help engineers make informed decisions that guide production.
Digital trains create virtual replicas of products, machines, and even whole manufacturing facilities, mirroring their physical counterparts. Using software like FlexSim, industrial engineering teams can run simulations to test performance and evaluate design changes before implementing them in the real world.
Through constantly refining your operational efficiency and product design, industrial engineering software helps reduce expenses and increase profits.
Industrial engineers are natural problem-solvers, and advanced software builds on their ability to find effective solutions. This ongoing focus on resource efficiency results in operations that are less wasteful and more sustainable—essential for our changing planet.
Industrial engineering software uses real-time data and analytics to predict when equipment needs maintenance. This proactive approach reduces unplanned downtime, prevents costly repairs, and extends equipment lifespan, keeping production schedules on track.
Get Inventor + AutoCAD + Autodesk Fusion + more—Professional-grade tools for product development and manufacturing planning.
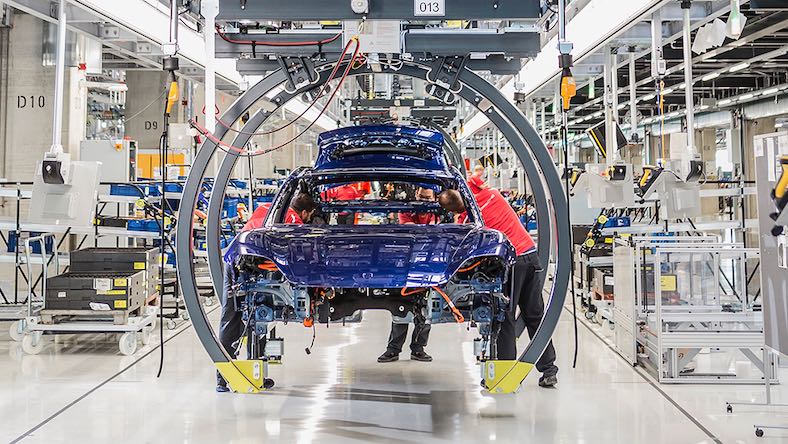
PORSCHE
To create its first fully electric sports car, the Taycan, Porsche’s industrial engineering team implemented digital factory planning to establish a cutting-edge, flexible facility in Stuttgart. This innovative setup includes driverless transport systems and a holistic resource and waste management approach.
Image courtesy of Porsche AG
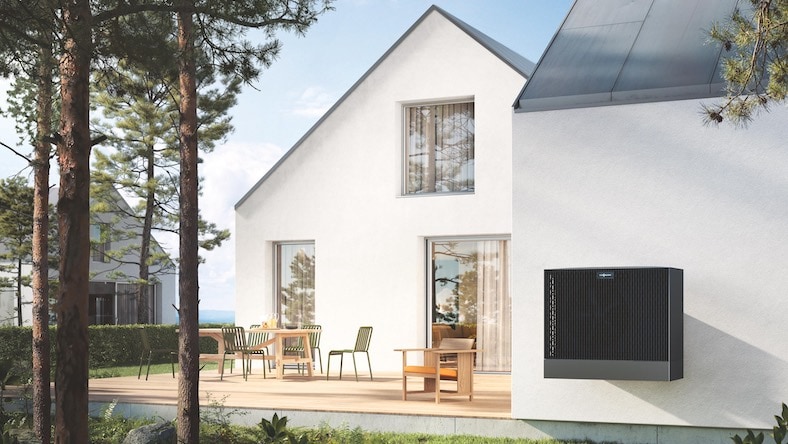
VIESSMANN
With demand for its heat pumps rising, Germany’s Viessmann designed a smart factory using digital factory planning and industrial engineering software. The facility automates production, assembly, and logistics and incorporates extended reality (XR) tools to visualize the factory’s digital twin.
Image courtesy of Viessmann
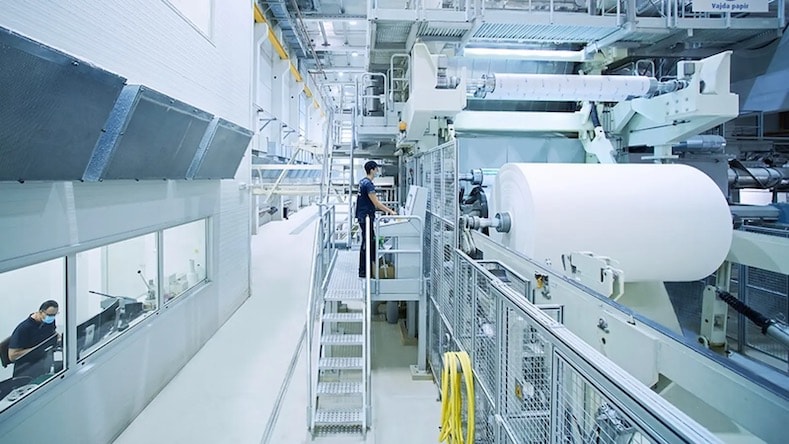
ANDRITZ
At the Austrian company ANDRITZ, industrial engineers design interconnected plants and machinery systems for several industries, including pulp and paper and metalworking. The Vajda Papir paper mill in Hungary integrated 3D-modeled digital twins of every component, using sensor data and AI to monitor the factory and prevent downtime while optimizing efficiency.
Watch this quick video to see how the manufacturing industry is on the verge of achieving more with fewer resources and a smaller environmental footprint, thanks to AI-assisted, cloud-connected industrial engineering software.
Discover how smart manufacturing digitises the factory floor using robotics, AI, and sensor data. This approach enhances design and sales processes and enables industrial engineers to increase productivity, competitiveness, and resilience against disruptions.
Industrialised construction offers a solution for industrial engineering teams in the building sector that are focused on sustainability. Applying lean manufacturing techniques to the design-and-build process helps reduce material waste and maximize resource efficiency.
Building a digital factory in well-planned phases allows industrial engineers to tailor production, gain agility, and improve their competitive edge. This approach also addresses waste reduction and other environmental challenges.
Learn about the growing role of AI in manufacturing through the use of ubiquitous sensor data, autonomous systems, robots, digital twins, and simulation-focused industrial engineering software. Embracing AI boosts speed, precision, and quality control.
Integrating machine learning into factory robotics is changing manufacturing. This technology enables industrial engineering teams to make processes more agile, customer-focused, efficient, safe, and profitable. Operations can adopt machine learning robotics gradually, seeing immediate improvements in assembly line configurations.
The future of industrial engineering will continue to find greater efficiencies and improvements to workforce conditions through a growing reliance on interconnected Industry 4.0 technologies such as robotics and AI/machine learning, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT) and edge computing, cloud computing and big data analysis, and other digital transformation technologies. Strengthening supply chains to be resilient to unforeseen fluctuations will also be important.
In addition, the trend of industrial engineers focusing on sustainability by improving eco-friendly processes, reducing waste, and encouraging social values will continue. Industrial engineering in manufacturing will play a key role in working toward a truly circular economy, where all products are durable, repairable, reusable, and/or recyclable.
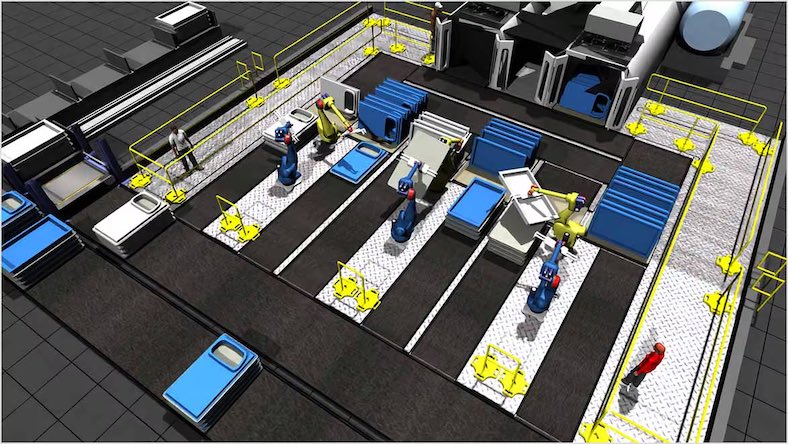
Industrial engineers use many specialized tools to continuously improve systems and processes. Starting at the top, facility layout design software lets industrial engineers practice digital factory planning to optimize the available space. Industrial robotics and other automated machinery streamline production, enable precision manufacturing, and reduce drudgery labor. Using integrated CAD/CAM/CAE software that’s cloud-connected to production hardware allows industrial engineers to dial in improvements to automated systems quickly based on data analysis.
Other important industrial engineering software tools include simulation software that lets engineers test complex processes virtually, yielding faster and less expensive insights, and manufacturing execution system (MES) software like Fusion Operations, which helps track processes and ensure quality control. Connected platforms like Autodesk Platform Services (APS) give industrial engineers access to data from multiple business systems and data sources via APIs and web services.
Industrial engineers work to continuously improve productivity, efficiency, and performance across industries. They do this by focusing engineering principles on systems such as supply chains and logistics; quality assurance, validation, and risk aversion; facility design and layout; workforce planning and safety, and process optimization.
Within each area, industrial engineers combine their technical know-how and problem-solving abilities with the complex data analysis and process simulation that’s possible using advanced industrial engineering software tools.
Industrial engineers often use computer aided design (CAD) software to create and optimize layouts for factories and processes. It helps visualize and improve workflows, equipment placements, and system designs before implementation.
Industrial engineering teams use various Autodesk software, including AutoCAD for design, Fusion for managing production and supply chain data, and simulation tools like FlexSim to model and test processes.