Worldwide Sites
You have been detected as being from . Where applicable, you can see country-specific product information, offers, and pricing.
Keyboard ALT + g to toggle grid overlay

What is circular design?
It’s design to support circularity—and a radical rethinking of how we use materials and energy. Components in products or buildings can be continually reused in future projects, with less waste. As the world’s resources become more limited, circular design is the foundation of the circular economy.
Benefits of circular design
Cut costs
Circular design helps you reduce costs in both design and production. You’ll need fewer materials, and you can benefit from a simplified supply chain with fewer spare parts in inventory.
Build brand reputation
When deciding what to buy, consumers increasingly weigh whether a company is responsible. With circular design, you can create more sustainable products that show your commitment to innovation.
Meet regulations
Plastic bans get the most attention, but product repair and “end-of-life” laws are also expanding in scope. Global operations require better data, designs, and collaboration to remain compliant.
Product design and manufacturing principles
-
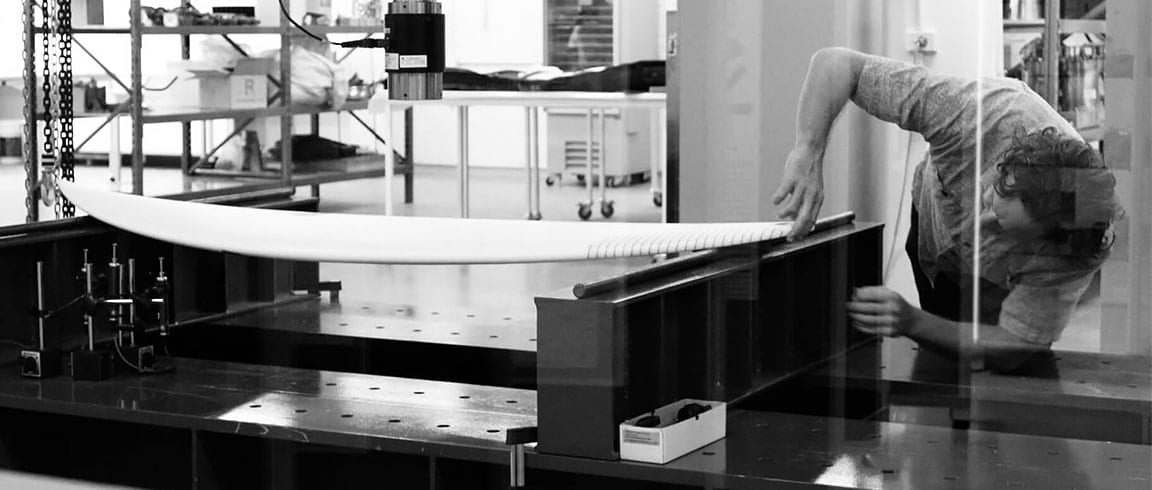
Lightweight and more durable
Use simulation in the design phase to ensure that your final products are optimized for mass and durability, with less waste.
-
Disassembly and reassembly
Design products and choose materials that make it easier to reuse parts, perform repairs, and recycle components.
-
Materials selection
Be mindful of the materials you select. Choose those that are less toxic, more recyclable, and whenever possible, recycled.
Architecture, engineering, and construction principles
-
Smart reuse
Existing building stock is valuable material. Making the most of existing structures through adaptive reuse avoids demolition waste, reduces procurement of new material, and can greatly lower a project’s embodied carbon.
-
Material tracking
Tracking the materials that go into a building is crucial, so that when it’s time to decommission, you’ll have all the origination data. This information is helpful in finding re-use or recycling options for materials.
-
Disassembly
Designing buildings to be easily disassembled and reused increases the likelihood that these structures will feed into the circular economy, producing less waste and keeping materials in circulation.
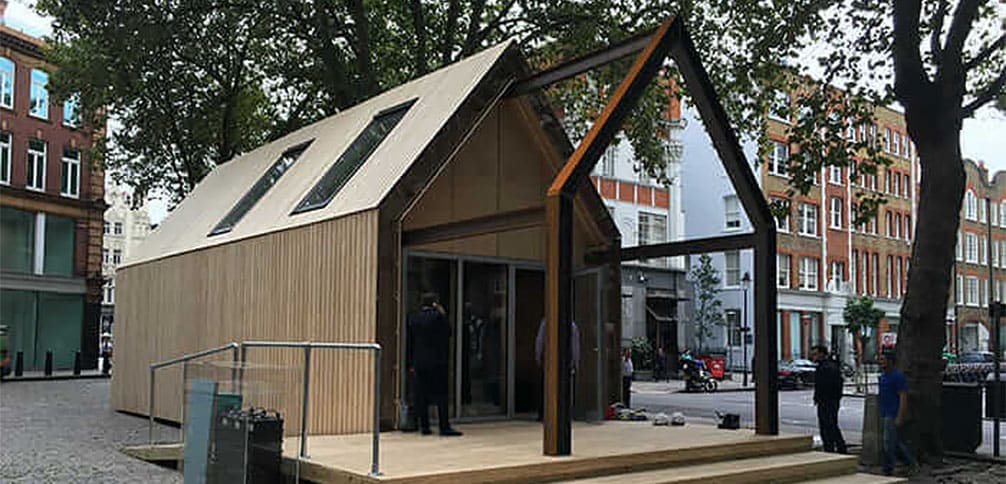

Architecture, engineering, and construction in action
Royal BAM builds, then totally deconstructs, a London house.
European construction group Royal BAM set out to test circular design principles in the real world. The firm designed and built an entire house in London, then deconstructed it after a short time to see if all the original materials could be reused.
Image courtesy of BAM
Product design and manufacturing software to help you get started
-
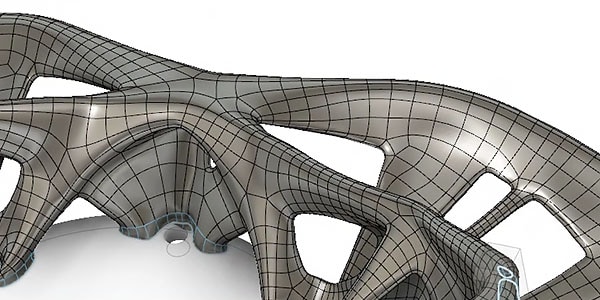
Better design
Fusion 360™ integrated software offers generative design capabilities to help you iterate and reduce weight, while maintaining structure and durability.
-
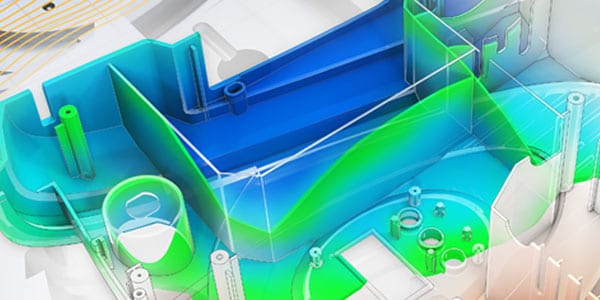
Better materials
Moldflow® software lets you simulate how greener, less toxic, recyclable or recycled materials will perform in a product.
-

Better management
Fusion Lifecycle facilitates collaboration across your entire ecosystem, keeping stakeholders aware of suppliers, materials, and compliance status.
-
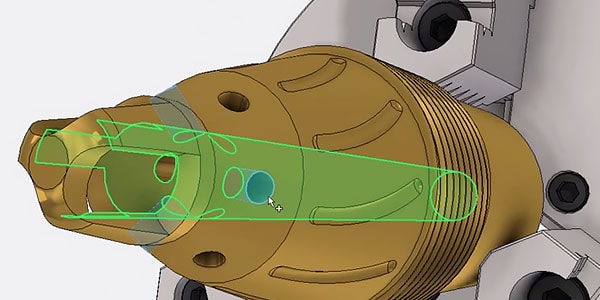
Comprehensive toolset
The Product Design & Manufacturing Collection offers comprehensive tools for better design and simulation, reducing material use, and improving durability.
Architecture, engineering, and construction software to help you get started
-

Better design
BIM 360 is a unified platform that helps project teams design and construct buildings that are simpler, less wasteful, and more easily disassembled.
-
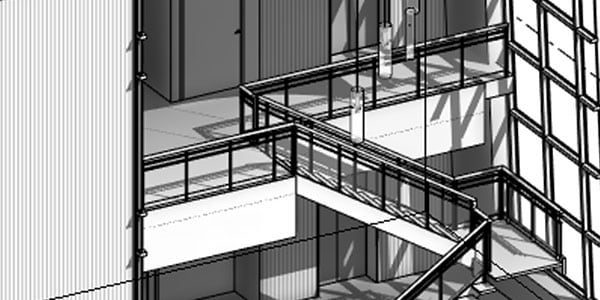
Comprehensive toolset
The Architecture, Engineering & Construction Collection helps you create intelligent 3D models with integrated BIM tools for design, infrastructure, and construction.
Learn more about sustainable design
-
Technology and sustainability
Technology for a sustainable world helps more companies improve productivity and achieve business goals.
-
Generative design
Deliver more innovative design and engineering solutions based on real-world constraints and requirements.
-
Generative design for sustainability
See how General Motors, Airbus, and other manufacturers use generative design to help meet sustainability goals.


